What is Cost Of Capital WACC Theory
 |
| What is Cost Of Capital WACC Theory |
Basic Concept :
What is Cost Of Capital WACC Theory
For a venture to be advantageous, the normal profit for capital must be higher than the expense of capital. Given various contending venture opportunities, speculators are relied upon to give their capital something to do with a specific end goal to augment the arrival. At the end of the day, the expense of capital is the rate of return that capital could be relied upon to win in the best option venture of equal danger. On the off chance that an undertaking is of comparative danger to an organization's normal business exercises it is sensible to utilize the organization's normal expense of capital as a premise for the assessment. Then again, for undertakings outside the center business of the organization, the present expense of capital may not be the suitable measuring stick to use, as the dangers of the organizations are not the same.
An organization's securities ordinarily incorporate both obligation and value, one must in this way compute both the expense of obligation and the expense of value to decide an organization's expense of capital. Vitally, both expense of obligation and value must be forward looking, and mirror the desires of danger and return later on. This implies, for occurrence, that the past expense of obligation is not a decent pointer of the genuine forward looking expense of obligation.
When expense of obligation and expense of value have been resolved, their mix, the weighted normal expense of capital (WACC), can be computed. This WACC can then be utilized as a markdown rate for a venture's anticipated money streams.
Cost of debt
At the point when organizations acquire stores from outside or take obligation from budgetary foundations or different assets the hobby paid on that sum is called expense of obligation. The expense of obligation is registered by taking the rate on a danger free security whose span coordinates the term structure of the corporate obligation, then including a default premium. This default premium will ascend as the measure of obligation increments (since, every single other thing being equivalent, the danger ascents as the expense of obligation rises).What is Cost Of Capital WACC Theory. Since as a rule obligation cost is a deductible cost, the expense of obligation is registered as an after assessment expense to make it practically identical with the expense of value (income are duty too). Hence, for gainful firms, obligation is reduced by the duty rate. The equation can be composed as (Rf + credit hazard rate)(1-T), where T is the corporate duty rate and Rf is the danger free rate.
Cost Of Equity :
The cost of equity is inferred by comparing the investment to other investments (comparable) with similar risk profiles. It is commonly computed using the capital asset pricing model formula:Cost of equity = Risk free rate of return + Premium expected for risk
Cost of equity = Risk free rate of return + Beta × (market rate of return – risk free rate of return)
where Beta = sensitivity to movements in the relevant market. Thus in symbols we have
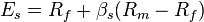
where:Es is the expected return for a security;Rf is the expected risk-free return in that market (government bond yield);βs is the sensitivity to market risk for the security;Rm is the historical return of the stock market; and(Rm – Rf) is the risk premium of market assets over risk free assets.
The risk free rate is the yield on long term bonds in the particular market, such as government bonds.
An alternative to the estimation of the required return by the capital asset pricing model as above, is the use of the Fama–French three-factor model.
Expected return
The expected return (or required rate of return for investors) can be calculated with the "dividend capitalizatio model", which is

The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets. The WACC is commonly referred to as the firm’s cost of capital. Importantly, it is dictated by the external market and not by management. The WACC represents the minimum return that a company must earn on an existing asset base to satisfy its creditors, owners, and other providers of capital, or they will invest elsewhere.

In the case where the company is financed with only equity and debt, the average cost of capital is computed as follows:

where D is the total debt, E is the total shareholder’s equity, Ke is the cost of equity, and Kd is the cost of debt. The market values of debt and equity should be used when computing the weights in the WACC formula. Hope you understand now What is Cost Of Capital WACC Theory. for further information please visit www.healthmakesfashion.com
Expected return
The expected return (or required rate of return for investors) can be calculated with the "dividend capitalizatio model", which is

The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the rate that a company is expected to pay on average to all its security holders to finance its assets. The WACC is commonly referred to as the firm’s cost of capital. Importantly, it is dictated by the external market and not by management. The WACC represents the minimum return that a company must earn on an existing asset base to satisfy its creditors, owners, and other providers of capital, or they will invest elsewhere.

In the case where the company is financed with only equity and debt, the average cost of capital is computed as follows:

where D is the total debt, E is the total shareholder’s equity, Ke is the cost of equity, and Kd is the cost of debt. The market values of debt and equity should be used when computing the weights in the WACC formula. Hope you understand now What is Cost Of Capital WACC Theory. for further information please visit www.healthmakesfashion.com
www.rapidtwist.com


Comments
Post a Comment